In this class, we will explain the static member, and how to use it in classes, variable, methods, and other members.
C# Static Members
In C#, static keyword can be used with classes, variables, properties, operators, methods, event and constructors. For classes, the static keywords will make it non-instantiable, meaning the class can’t have an instance. The new keyword cannot be used to create an instance of a static class. The methods, properties and other members in that class can be accessed by having the name of the class preceding the method or property. Example:
MyStaticClass.MyStaticMethod;
Syntax of Static Class in C#
static class ClassName
{
}
Example of Static Class in C#
static class TutorialsPanelStaticMembers
{
public static string Concat(string a, string b)
{
return a + " " + b;
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(TutorialsPanelStaticMembers.Concat("Tutorials", "Panel"));
Console.ReadKey();
}
Output:

Note: only static members can be declared in a static class. However, no-static class can have static members. The code below will throw an exception:
static class TutorialsPanelStaticMembers
{
public static string Concat(string a, string b)
{
return a + " " + b;
}
public string Name;
}
Error:
MyProject.TutorialsPanelStaticMembers.Name’: cannot declare instance members in a static class
Static Constructors
In contrary of non-static constructors, a static constructor is used to initialize the class itself. In non-static class, a Non-static constructor is to be used to initialize an instant of that class.
In C#, a static constructor is called automatically before any static members are referenced. It cannot have a parameter, doesn’t not have a access modifier, and cannot be called directly.
Example of Static Constructor in C#
namespace CSharpConsoleApp
{
public class ProgrammingTutorials
{
// Static Constructor
static ProgrammingTutorials()
{
Console.WriteLine("Static Constructor");
}
// Default Constructor
public ProgrammingTutorials()
{
Console.WriteLine("Default Constructor");
}
}
}
Now call both Constructors from the main method:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// both Default Static constructors will be invoked for the first instance
ProgrammingTutorials _tutorials1 = new ProgrammingTutorials();
// only Default constructor will be invoked
ProgrammingTutorials _tutorials2 = new ProgrammingTutorials();
Console.ReadKey();
}
Output:
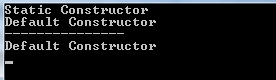
Note: Static keyword cannot be used with indexers, destructors or types other than classes.

Comments